SBE Office IT System
Options:
Options:
Options:

A typical IT system for SBEs with one or more workgroups of few workstations, and basic needs for applications, file storage, and security is displayed here. There is no need for a server in the office, since providers offer similar services in the Cloud (over the Internet), such as Microsoft 365©. A Fast Ethernet switch will be needed for a cabled network where all cables connect to it. A Network Attached Storage (NAS) device will be used to store shared files locally, with the capability to synchronize them to the Cloud. An external hard disk (HDD), directly connected to the NAS via USB, will serve as backup storage.
It is wise to invest in a Firewall device, even an entry-level one, which would be better than the basic Firewall included with a modem/router. This Firewall will scan and filter (almost) everything accessed on the Internet, and if it finds a threat, it will stop it before it reaches the workstations. The modem/router connects the local network to the Internet using a Broadband link. Usually, this device is supplied by the Broadband provider (ISP).

Currently, telecommunication providers worldwide have replaced the old PSTN analogue phone system with a modern digital one. This new system works through the Internet and is called Voice over IP (VoIP). To use VoIP, an office must have an IP phone connected to the network.
It is also necessary to have a multifunction device that includes a printer and scanner to import and export documents to and from paper.
Nowadays, people often work from home or other remote locations. There are several cost-effective ways to enable this, e.g. with Remote Desktop.
The modem/router usually comes with Wi-Fi capabilities, which smartphones and visiting laptops can use. However, it is not recommended to rely heavily on it, because Wi-Fi can be hacked. It is better to use a more secure Wi-Fi system (select ‘Firewall with Wi-Fi’ to read more).
Sometimes a local server is needed to meet the needs of an office, whether small or large. This typically happens when a business needs to use a local database and/or another shared application. A local server is also needed if enhanced security and control over users and assets are necessary.
When an office uses a local server, an external HDD is not needed, since the main local storage moves from the NAS to the server, and the NAS serves as one of the backup destinations itself.
A good Firewall device is an important asset for any size of business. By using a Firewall with Wi-Fi, the main Wi-Fi access point is moved from the modem/router to the Firewall device. In this way, Wi-Fi becomes more secure, and the Firewall provides wireless network management and better control. Read more about a Wireless IT System (this will close the current document)…

Often, other peripheral devices need to be connected to an office network. Wi-Fi access points are such devices. If the office needs an extended wireless network or if the wireless needs are not fully met by the Firewall’s built-in Wi-Fi, at least one standalone Wi-Fi access point should be installed to provide wider Wi-Fi coverage and higher speeds on the wireless network.
Businesses often need to enhance office security. The best starting point is to invest in surveillance cameras. Nowadays, these cameras (IP cameras) are connected directly to the local network, allowing access from any local PC or remotely. It is possible to record the video feed from the cameras on Cloud servers (recommended) or on local storage.

Several devices such as Wi-Fi access points, IP cameras, and IP phones do not need a separate power adapter. Instead, they can receive power directly through their network cable. These devices are compatible with Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology. For this method to work, the network switch must also support PoE technology, because it is the network switch that injects electric power into the Ethernet cable.
Sometimes we have to start small before we grow big. In this case, typically only one personal computer or laptop is needed in the business office. The most important factor is to have a broadband to at least use cloud services and exchange emails. The personal computer can connect directly, via a network cable (Ethernet), to the modem/router provided by the Internet Service Provider (ISP). The modem/router also includes a basic Firewall that defends against some basic threats. One external HDD will be needed to save backups from the PC, connected directly via a USB cable. A multifunction device (printer/scanner) and an IP phone (VoIP) complete such a small office.
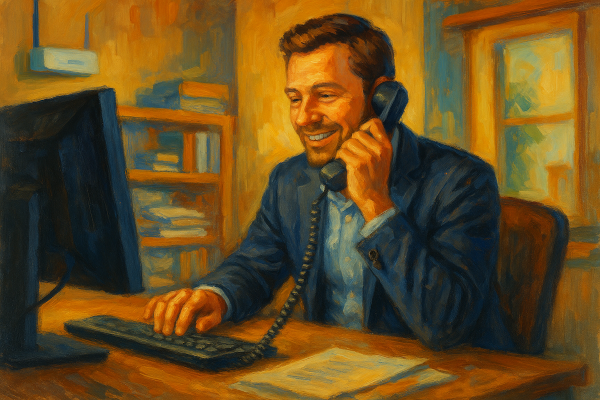

Similar to an Ethernet cabled network in a small office, a wireless network will serve an IT system with basic needs for applications, file storage, and security. Here also there is not need for a server in the office, instead it is cost effective to use similar services in the Cloud such as Microsoft 365©. In a wireless system there is also a network switch (maybe smaller than if the network was wired), and is used mainly to connect the devices on the network backbone, e.g. the NAS with an external USB HDD, a server if needed, the Wi-Fi firewall device and the Wi-Fi access points. In a wireless network it is recommended to use as the main access point, the one that is included in the firewall device, or standalone access point(s) with good security. The network switch could also supply power to the access points using PoE. A modem/router here is also needed, to provide the broadband link to the Internet.
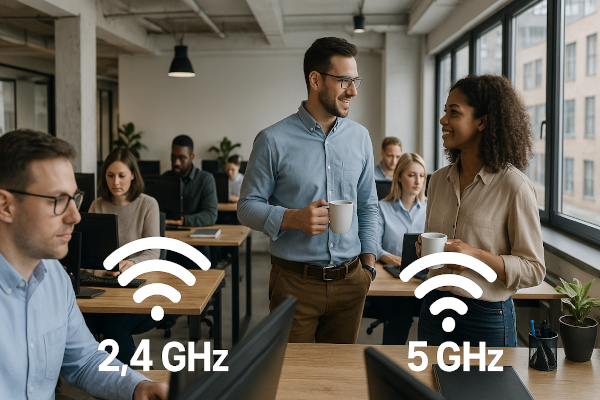

The Wi-Fi frequency works in two different bands, at 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Currently, the 6GHz band introduced as well. The 2.4 GHz band provides longer-range coverage but transmits data at slower speeds. The 5 GHz band offers less coverage but transmits at faster speeds. The 6 GHz band provides the least coverage but transmits data at superfast speeds. A password and a SSID (service set identifier) must be used on the access points as well as on each Wi-Fi device. A firewall with wireless management capabilities is recommended, this service provides also seamless roaming between access points. Nowadays inexpensive Cloud based wireless management is also available.
It is very important to remember, that a wireless network is not as secure as a wired one. In the past was recommended not to use a wireless network unless extra security was used such as Wi-Fi Protected Access Enterprise mode, to read more click on ‘Wi-Fi Security’ and read further below.
Other devices similar to the cabled network, are a multifunction printer (with scanner), the IP phones (VoIP) and if needed IP cameras. All the devices on the front end can be connected using the Wi-Fi.

Whatever is the size of an office, in a wireless network if a local server is installed it must be wired with an Ethernet cable to the network switch. It is not recommended to use wireless server for several reasons, such as problems created with the network sessions. A local server can be used for a local database and/or other shared applications, as well as to enhance security and control over users and assets.
When an office uses a local server, an external HDD is not needed, since the main local storage moves from the NAS to the server, and the NAS serves as one of the backup destinations itself.
Using a wireless network instead of a wired one, may save cabling costs and it is also easier to be implemented. However, hasn’t got the benefits of a wired network such as, 1) very low latency and 2) security against direct external hacking. Because of the former reason, currently is not recommended to use Wi-Fi for the network backbone e.g., servers, shared storage, access points, etc. For the latter reason, when wireless network is used, one must have in mind the following security issues.

Wi-Fi version 6 (ax) or 6E and later should be used, since it comes with WPA 3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access version 3) security protocol. This protocol offers encryption with AES-128 (Advanced Encryption Standard with 128 bits size) in Personal mode, together with Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) exchange. This method of authentication between Wi-Fi devices is new and more secure than the previous methods. WPA 3 in Enterprise mode has an encryption with AES-192 and AES-256 with advanced technologies. A small business most likely will use Personal mode, since Enterprise mode has higher costs and needs RADIUS server, on a wireless management device or on a server. RADIUS server provides users with password or user certificates. Nowadays wireless management on Cloud supporting Enterprise mode started to be offered from several vendors.
In a wireless network the Wi-Fi access points play an essential role. They extend a small wireless network to a wider area, they provide more speed if the network’s needs increase. With a wireless management, it doesn’t matter how many access points are there, since they can be used as a Mesh network with seamless roaming for the users, (entry level APs may no have this technology). This kind of management doesn’t necessary needs a separate device or a Cloud service, business grade access points are managed between themselves. It is recommended to have the access points wired to the network backbone, but they also can be connected wireless to a firewall device with Wi-Fi. If the access points are wired to a network switch, they could also use Power over Ethernet if it is available.
In a wireless as in a wired network, businesses need office security. A cost effective way is to install IP cameras for surveillance and recording. In a wireless network IP cameras are often used wireless to save cabling costs, assuming that there is a power point near to them, if there is not a local power socket than they must be wired and use PoE. It is possible to record the video feed from the IP cameras on Cloud servers (recommended) or on local storage.
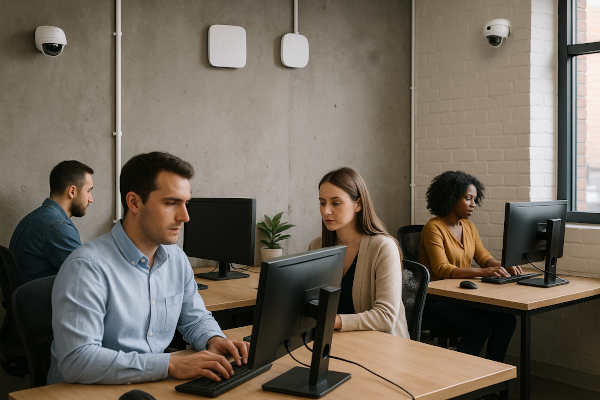

Power over Ethernet (PoE) can be also used with wireless network since anyway a switch will needed for the backbone. The PoE compatible switch can provide power to Wi-Fi access points. Other devices such as IP cameras or IP phones can also use PoE but maybe is more convenience to use them as wireless devices.
Sometimes we have to start small before we grow big. In this case, ‘in’ a wireless setup, typically only one Laptop with Wi-Fi is needed in the business office. The most important factor is to have a broadband to at least use cloud services and exchange emails. The Laptop can connect directly, via the Wi-Fi, to the modem/router provided by the Internet Service Provider (ISP). The modem/router also includes a basic Firewall that defends against some basic threats. One external HDD will be needed to save backups from the Laptop, connected directly via a USB cable. A multifunction device (printer/scanner) and an IP phone (VoIP) complete such a small office. In this case where a Laptop is used, able to move it between home and office, a remote PC doesn’t needed.

Small businesses should not hold back, and in practice cannot afford to be less efficient than large enterprises when it comes to their IT System. The daily challenges they face, compel them to stay at the forefront of technology, adopt Best Practices , and operate on par with larger organizations.
 Small offices with one or more Workgroups utilize Applications and Services installed on the workstations.
Small offices with one or more Workgroups utilize Applications and Services installed on the workstations. Workstations should be protected by Antivirus software.
Workstations should be protected by Antivirus software. Remote Desktop Host should be enabled on selected workstations to support remote access.
Remote Desktop Host should be enabled on selected workstations to support remote access. A Digital Signature Certificate , purchased from a Trusted Certificate Authority (CA), enables users to digitally sign documents locally.
A Digital Signature Certificate , purchased from a Trusted Certificate Authority (CA), enables users to digitally sign documents locally. A Local Server primarily runs installed Applications and Services.
A Local Server primarily runs installed Applications and Services. Shared Storage on the server allows users to share files; in this case, a NAS may not be required.
Shared Storage on the server allows users to share files; in this case, a NAS may not be required. File Versioning can be enabled via Shadow Copies on Microsoft Servers.
File Versioning can be enabled via Shadow Copies on Microsoft Servers. File Synchronization with the cloud is recommended for improved data security.
File Synchronization with the cloud is recommended for improved data security. The Server should be protected by Antivirus software.
The Server should be protected by Antivirus software. Dual Backup is recommended, one to a local NAS and one to a remote or cloud destination.
Dual Backup is recommended, one to a local NAS and one to a remote or cloud destination. A DNS Server with Forwarding handles name resolution and forwards unresolved requests to Online DNS Servers.
A DNS Server with Forwarding handles name resolution and forwards unresolved requests to Online DNS Servers. A DHCP Server on the local server assigns IP addresses to clients.
A DHCP Server on the local server assigns IP addresses to clients. A Local Database can be hosted on the server to meet business data needs.
A Local Database can be hosted on the server to meet business data needs. Microsoft Active Directory can be installed on the server to manage users, devices, and other resources. It can also sync with Microsoft Entra ID for cloud integration.
Microsoft Active Directory can be installed on the server to manage users, devices, and other resources. It can also sync with Microsoft Entra ID for cloud integration. In ServerLess environments, a NAS provides Shared Storage for user file access.
In ServerLess environments, a NAS provides Shared Storage for user file access. File Synchronization between NAS and cloud services is advised.
File Synchronization between NAS and cloud services is advised. Dual Backup from NAS, one to a local external hard disk and one to a remote or cloud location is recommended.
Dual Backup from NAS, one to a local external hard disk and one to a remote or cloud location is recommended. Serves as a Storage destination for local NAS backups.
Serves as a Storage destination for local NAS backups. The external hard disk can be also used as a Backup Archive for backed up data.
The external hard disk can be also used as a Backup Archive for backed up data. Network Security such as access restrictions, and password protection is essential.
Network Security such as access restrictions, and password protection is essential. Ethernet cabling using a Star Topology, is the most common local network configuration.
Ethernet cabling using a Star Topology, is the most common local network configuration. If wireless access is provided on the FrondEnd, Wi-Fi 6 with WPA3 security should be the minimum standard.
If wireless access is provided on the FrondEnd, Wi-Fi 6 with WPA3 security should be the minimum standard. Provides primary Firewall protection against external threats.
Provides primary Firewall protection against external threats. Includes a DNS Proxy to handle name resolution for clients. Only one DNS service should operate on the local network, either on the firewall or the server.
Includes a DNS Proxy to handle name resolution for clients. Only one DNS service should operate on the local network, either on the firewall or the server. Includes a DHCP Server. Only one DHCP service should be active, either on the firewall or the server.
Includes a DHCP Server. Only one DHCP service should be active, either on the firewall or the server. Hardware firewall should include Antivirus & Malware Filtering – many vendors offer affordable options.
Hardware firewall should include Antivirus & Malware Filtering – many vendors offer affordable options. Content Filtering blocks access to harmful or unauthorized websites.
Content Filtering blocks access to harmful or unauthorized websites. A built-in VPN Server supports secure remote connections by creating a VPN Tunnel over public networks.
A built-in VPN Server supports secure remote connections by creating a VPN Tunnel over public networks. If multiple access points are used, Wi-Fi Management helps maintain security and seamless connectivity.
If multiple access points are used, Wi-Fi Management helps maintain security and seamless connectivity. Can host a Basic Firewall if a dedicated hardware firewall is not available, not ideal for busy offices.
Can host a Basic Firewall if a dedicated hardware firewall is not available, not ideal for busy offices. A router can host the DNS Proxy if no server or hardware firewall provides it.
A router can host the DNS Proxy if no server or hardware firewall provides it. A router can host the DHCP Server if no server or hardware firewall provides it.
A router can host the DHCP Server if no server or hardware firewall provides it. VoIP (Voice over IP) nowadays is the standard for office telephony.
VoIP (Voice over IP) nowadays is the standard for office telephony. A Multifunction printer/scanner supports paper-to-digital and digital-to-paper workflows.
A Multifunction printer/scanner supports paper-to-digital and digital-to-paper workflows. Multiple Wi-Fi Access Points may be required for wireless coverage.
Multiple Wi-Fi Access Points may be required for wireless coverage. Surveillance systems, when connected to the network, offer remote monitoring capabilities.
Surveillance systems, when connected to the network, offer remote monitoring capabilities. Broadband provides the link between the local network and the Internet.
Broadband provides the link between the local network and the Internet. DNS NameServers enable IP-to-domain name resolution.
DNS NameServers enable IP-to-domain name resolution. Online Services like Website Hosting support both basic and advanced business functions.
Online Services like Website Hosting support both basic and advanced business functions. Trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) issue Digital Certificates for secure document signing and identity verification, such as with HTTPS on secure websites.
Trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) issue Digital Certificates for secure document signing and identity verification, such as with HTTPS on secure websites. Online Digital Signature Services allow secure document signing without owning a certificate.
Online Digital Signature Services allow secure document signing without owning a certificate. Online Storage enhances data protection and enables remote access.
Online Storage enhances data protection and enables remote access. File Versioning often included with cloud storage, helps protect against accidental changes.
File Versioning often included with cloud storage, helps protect against accidental changes. File Synchronization Host keeps files updated between local and cloud environments.
File Synchronization Host keeps files updated between local and cloud environments. Backup for Cloud Storage and Mailboxes is essential.
Backup for Cloud Storage and Mailboxes is essential. An Online Email Server is the recommended solution for SMBs.
An Online Email Server is the recommended solution for SMBs. Microsoft Entra ID provides cloud based directory services.
Microsoft Entra ID provides cloud based directory services. An Online Database, such as Microsoft Azure SQL, can meet SMB data needs.
An Online Database, such as Microsoft Azure SQL, can meet SMB data needs. A Remote Desktop client allows users to access office workstations from remote locations.
A Remote Desktop client allows users to access office workstations from remote locations. A VPN Client provides secure connectivity to the office network.
A VPN Client provides secure connectivity to the office network.
The IT system includes a Local Server. Removing the Hardware Firewall is not recommended, as it would significantly reduce the overall security of the system.
Please use the email form below to send us an email.
NetBuddy.net and NetBuddy.co.uk are websites operated by Netbuddy Ltd, a company registered in England, U.K.
When you submit your email, or when you are subscribing to our newsletters, you agree to allow your email address to be saved in cookies. These cookies are used for the proper functioning of the subscription form.
When you visit our website for the first time, an appropriate widget will display a GDPR- and CCPA-compliant notification and may also set cookies. These tools provide you with the option to accept or reject cookies.
When visitors send a message through this site, we collect the data entered in the form, along with the visitor’s IP address and browser user agent string. This information may be used for spam detection.
This site may include embedded content (e.g., Google scripts, cookies widget, security widgets). Embedded content from third-party providers behaves in the exact same way as if you had visited the third-party websites directly.
These third parties may collect data about you, use cookies, embed additional tracking technologies, and monitor your interactions with their content on our site, including anonymous tracking of your engagement, without storing personally identifiable information.
We do not share your data with anyone outside of our organization.
If you send us a message via the site, the message and its metadata may be retained indefinitely.
For users who subscribe to our newsletters, we may store their email addresses indefinitely or until a written request for deletion is received. Subscribers can unsubscribe at any time.
Visitor messages may be screened through a remote and automated spam detection service.
If you have subscribed or sent a message via this site, you may request an exported file of the personal data we hold about you, including any information you provided. You may also request the permanent deletion of your personal data. This does not include any data we are required to retain for administrative, legal, or security purposes.